With the widespread adoption of e-commerce channels, fraudulent activity and losses have increased across the board. Businesses that want to prevent fraud and reduce chargebacks will need to rely on advanced fraud prevention and identity trust solutions to save time and money. One tool to consider: digital identity verification. Let’s explore some common questions about digital identity verification: what it is, how it works, why it’s necessary, and how to get it for your business.
What is digital identity verification?
Digital identity verification is the process by which a business verifies the trustworthiness of a customer’s digital identity in an e-commerce transaction. The business may do this with a fraud prevention solution that can verify that a customer is who they say. The solution compares the information the customer provides or activity they’re engaging in to previous information or activity.
The more a customer provides the same information or performs the same activity, the better the solution can verify their identity. When that customer performs a new activity or provides new information, the solution connects those identity elements to their identity trust profile. Over time, the solution will learn to detect when a bad actor may be using that customer’s information fraudulently.
Fraud prevention solutions in digital identity verification may include a global network of fraud and trust-related signals linked by AI and machine learning. These components compare a customer’s information and activity from across the web to complete their identity trust profile.
How does digital identity verification work?
Four components make digital identity verification work in e-commerce transactions. When businesses combine these four components, they can verify a customer’s digital identity to prevent fraud, accept more good orders, reduce manual reviews, and manage business outcomes.
- A global network of fraud and trust-related signals
- Supervised machine learning
- Unsupervised machine learning
- Advanced AI
A global network of fraud and trust-related signals is essential for digital identity verification. When a customer performs an activity or provides information, such as making a purchase or creating an account, their identity elements join a network. Identity elements include usernames, email addresses, credit card numbers, payment information, IP addresses, device data, and more. The network can include billions of interactions from online transactions across countries and industries.
The right digital identity verification company can give businesses access to networks and data they wouldn’t have otherwise. However, the data in a network alone is powerless without machine learning and advanced AI to link it all together.
Machine learning helps the global network learn about each customer. Supervised machine learning analyzes billions of historical transactions from the global network and looks for past fraud and trust-related signals. Unsupervised machine learning uses advanced algorithms to detect transaction anomalies and emerging fraud attacks.
Advanced AI links identifier data from transactions and interactions from across the web. This link between AI and a global network simulates an experienced fraud analyst. It gives businesses a more complete picture of each customer’s level of identity trust.
How to verify someone’s identity
Let’s look at an example of how to verify someone’s digital identity with a global network, machine learning, and advanced AI. Say a customer wants to buy jewelry with an online merchant. Given the high value of the item, there’s a good chance the customer has only shopped with the business once or twice — if at all. The customer researches the piece they want, creates an account with the merchant, and completes their transaction online.
Unfortunately for the merchant, this is a new or little-known customer, so they may have limited digital identifier data. Not having that data means the merchant doesn’t know if the customer is a bad actor placing an order with a stolen credit card. That risk opens up the business to inventory loss, chargebacks, and a tarnished reputation.
A digital identity verification solution that uses a global network, machine learning, and advanced AI can tell if any part of the customer’s activity is potentially fraudulent. And it can compare certain elements of the customer’s digital identity — username, credit card number, address, device, etc. — to other transactions from across the web. Comparing these elements can help businesses determine the trustworthiness of the digital identity that’s engaging with them online.
What makes up a digital identity?
A digital identity is a digital collection of identity attributes. A digital identity may be any information a customer has volunteered to a company or entity online. Customers build their digital identity at any point in their buying journey, including when they open an account, engage in a loyalty program, or make a purchase. Attributes may break down into four categories: payment data, location data, digital identifier data, and unique customer data.
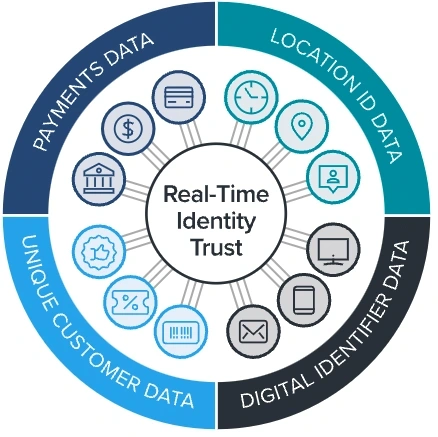
- Payment data includes banking information, credit or debit card numbers, and loyalty point or account numbers.
- Location data includes geolocations, IP addresses, and physical addresses.
- Digital identifier data includes trusted devices, email addresses, usernames, and phone numbers.
- Unique customer data is anything a business knows about their customers. This might include their average transaction size, how often they buy products, and where they buy products.
Why is digital identity verification necessary?
Digital identity verification is ideal and necessary for any business that participates in e-commerce and wants to reduce losses from payments fraud and chargebacks. Since the coronavirus pandemic accelerated the adoption of e-commerce in 2020, most businesses saw a significant increase in online transactions and fraud.
Many businesses responded to that increase in fraud by tightening business policies around order acceptance. Unfortunately, businesses may be declining between 15% and 20% of CNP transactions to prevent fraud losses. By the end of 2021, those false positives will account for $443 billion in lost revenue, according to an Aite Group estimate. Digital identity verification can prevent those losses significantly. And it can give businesses confidence that they’re accepting as many good orders as possible.
In particular, the future of digital identity verification is in the mobile channel, an attractive target for bad actors. Banks, financial services, insurance providers, and retailers may be unprepared for sophisticated fraud attempts over mobile channels. In the mobile channel, businesses should be wary of any digital identity verification solution that increases friction for good customers.
What services does a digital identity verification company provide?
A digital identity company creates, maintains, and manages identity information for businesses. These companies are an essential part of any business’s fraud prevention strategy, as verifying a digital identity goes hand in hand with fraud detection. In addition, companies may supply multi-factor authentication services. These services further verify if the customer a business is interacting with can access the email account or smartphone associated with the account.
The ideal digital identity verification company can give businesses access to a global network of fraud and trust-related signals linked by advanced AI and machine learning. It can help verify the trustworthiness of a digital identity, flag suspicious activity, and produce a safety score for each transaction. This safety score may be based on the business’s unique transaction standards and operational goals. The result is fewer chargebacks from friendly and criminal fraud, fewer manual reviews, and reduced friction in the customer journey.